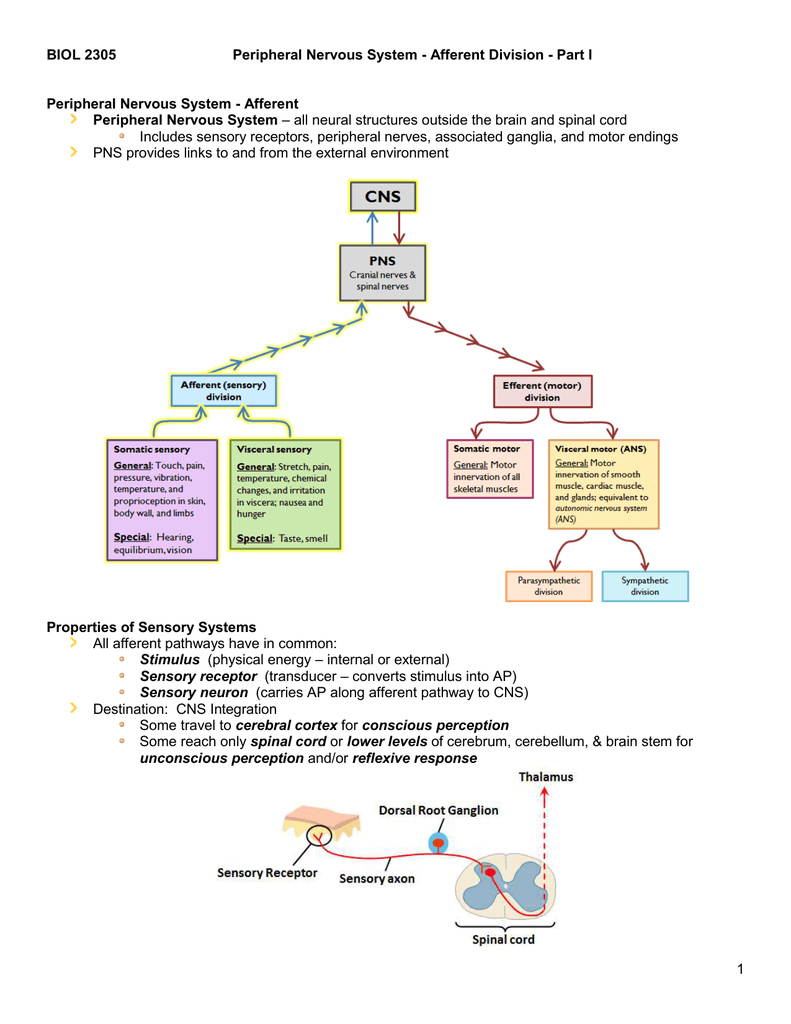
The Sensory (afferent) Division Of The Peripheral Nervous System
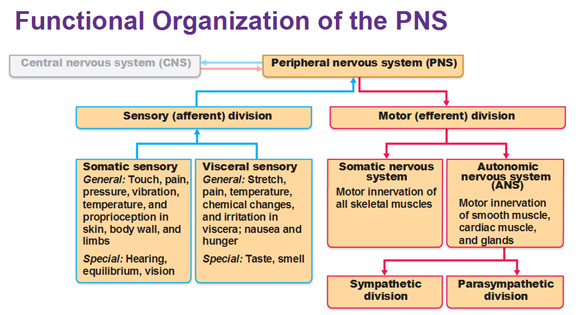
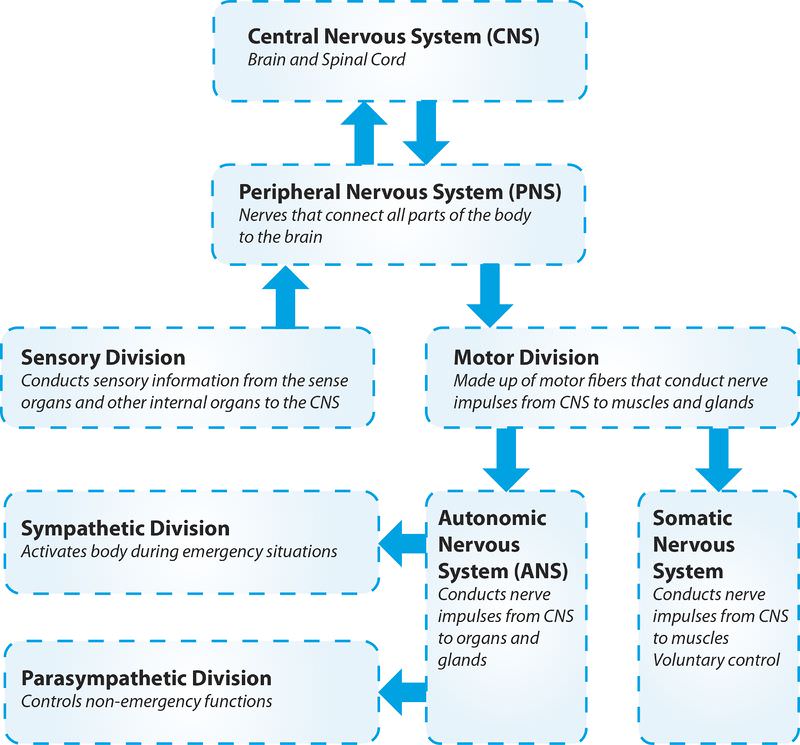
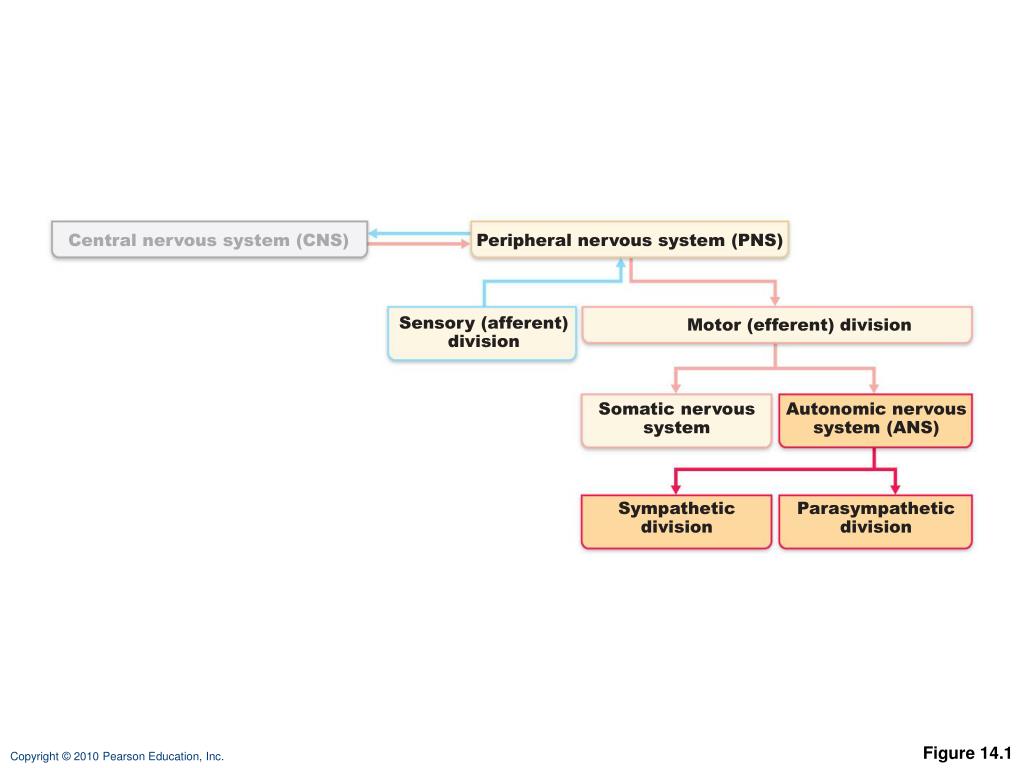
The sensory (afferent) division of the peripheral nervous system. It can be further subdivided into somatic and visceral divisions. The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body Changes stimuli Integration To process and interpret sensory input and decide if action is needed Motor output A response to integrated stimuli The response activates muscles or glands Structural Classification of the Nervous System Central. To understand the concepts related to the nervous system read through the short lesson called Afferent Division of the Peripheral Nervous System.
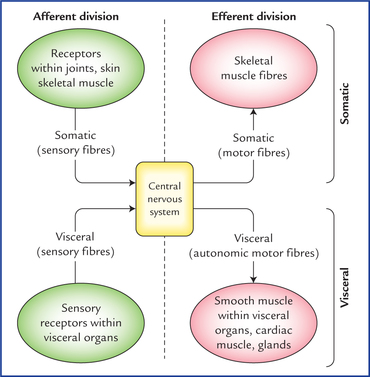
Similarly what are two subdivisions of the efferent nerves. Sensory nerves contain only afferent fibers long dendrites of sensory neurons. The sensory division collects information touch pain pressure vision taste etc from outside somatic sensory and inside visceral sensory of.
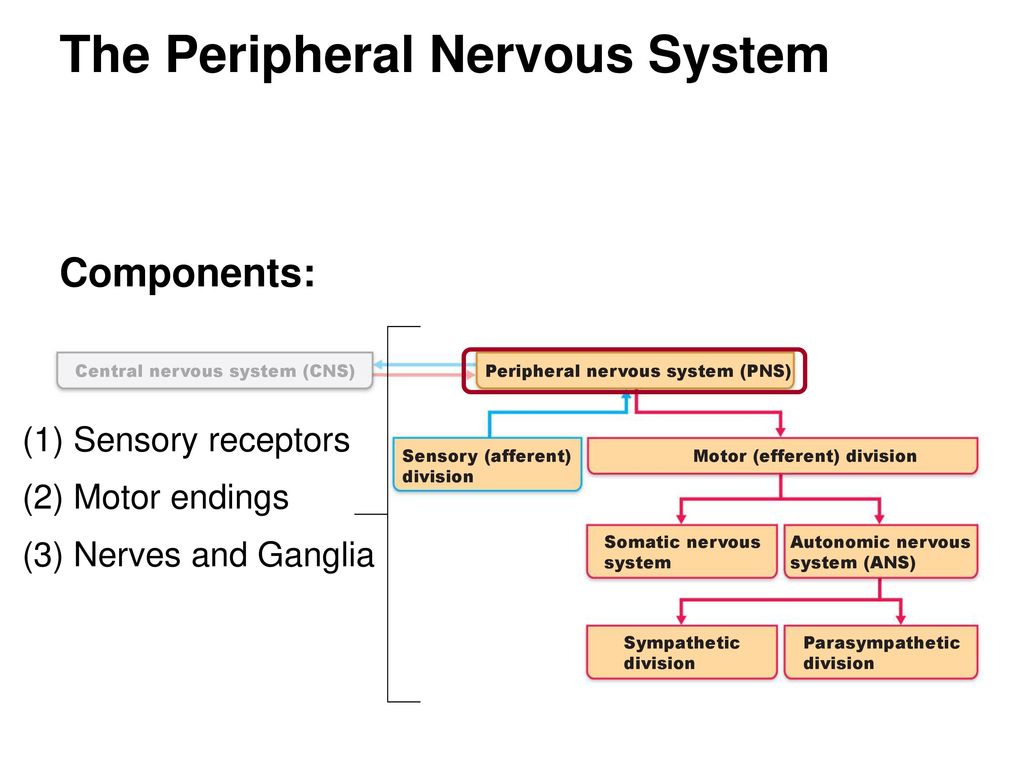
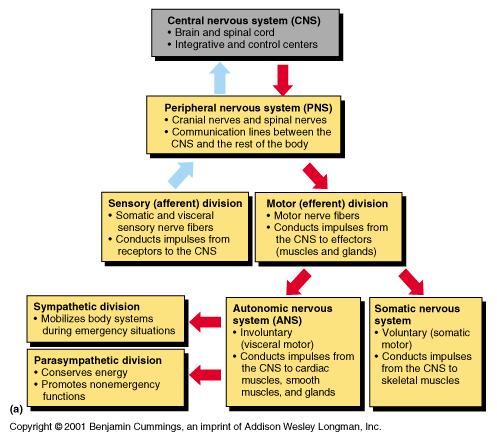
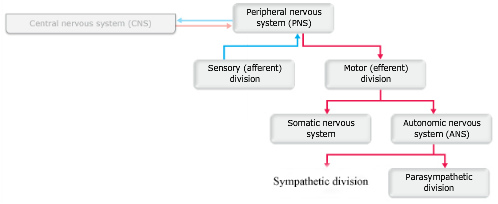
The ANS is responsible for providing sensory and motor innervation to smooth muscles blood vessels glands and internal organs. The Peripheral Nervous System Ganglia are collections or small knots of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS. The peripheral nervous system is further subdivided into an afferent sensory division and an efferent division.
Finally the efferent or motor division is again subdivided into the somatic nervous. Many visceral organs are supplied with fibers from both divisions. The sensory division collects information touch pain pressure vision taste etc from outside somatic sensory and inside visceral sensory of.
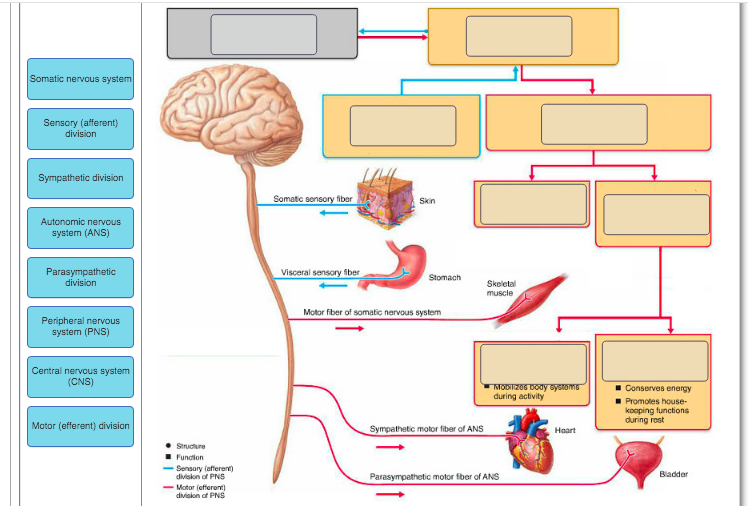
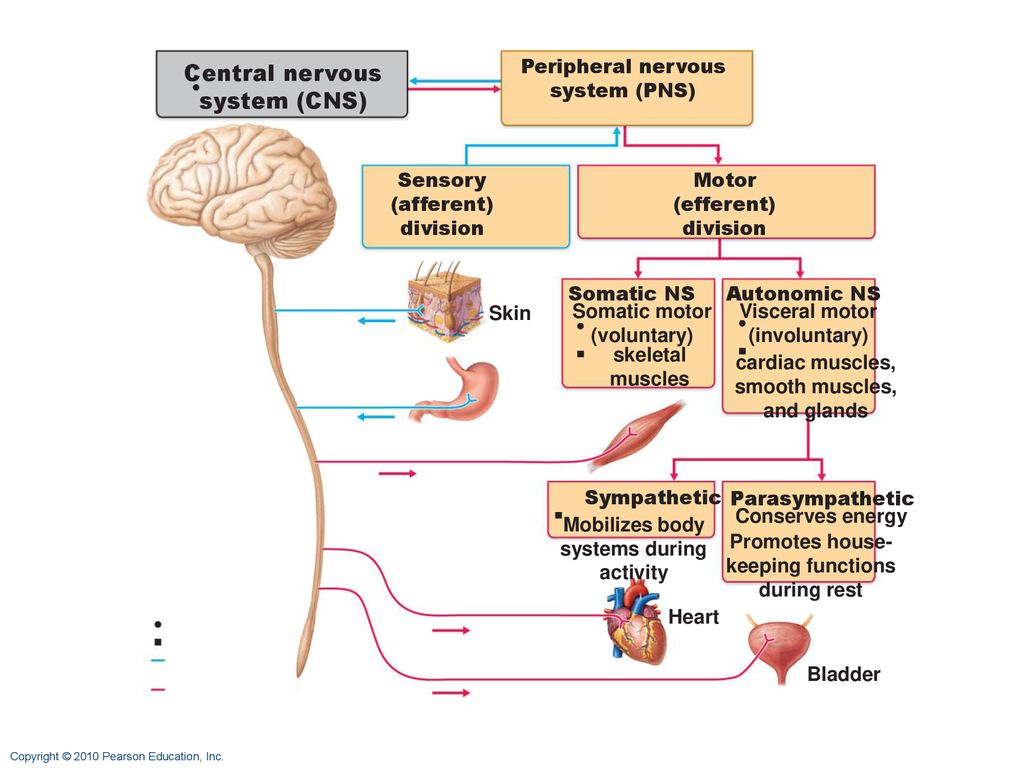
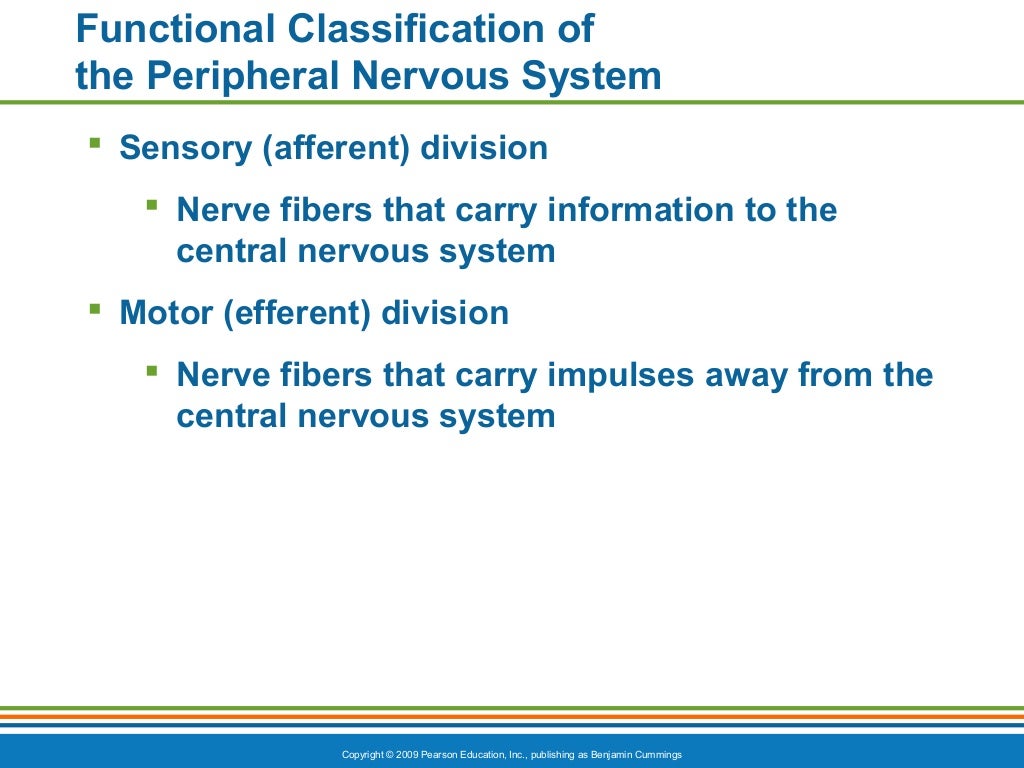
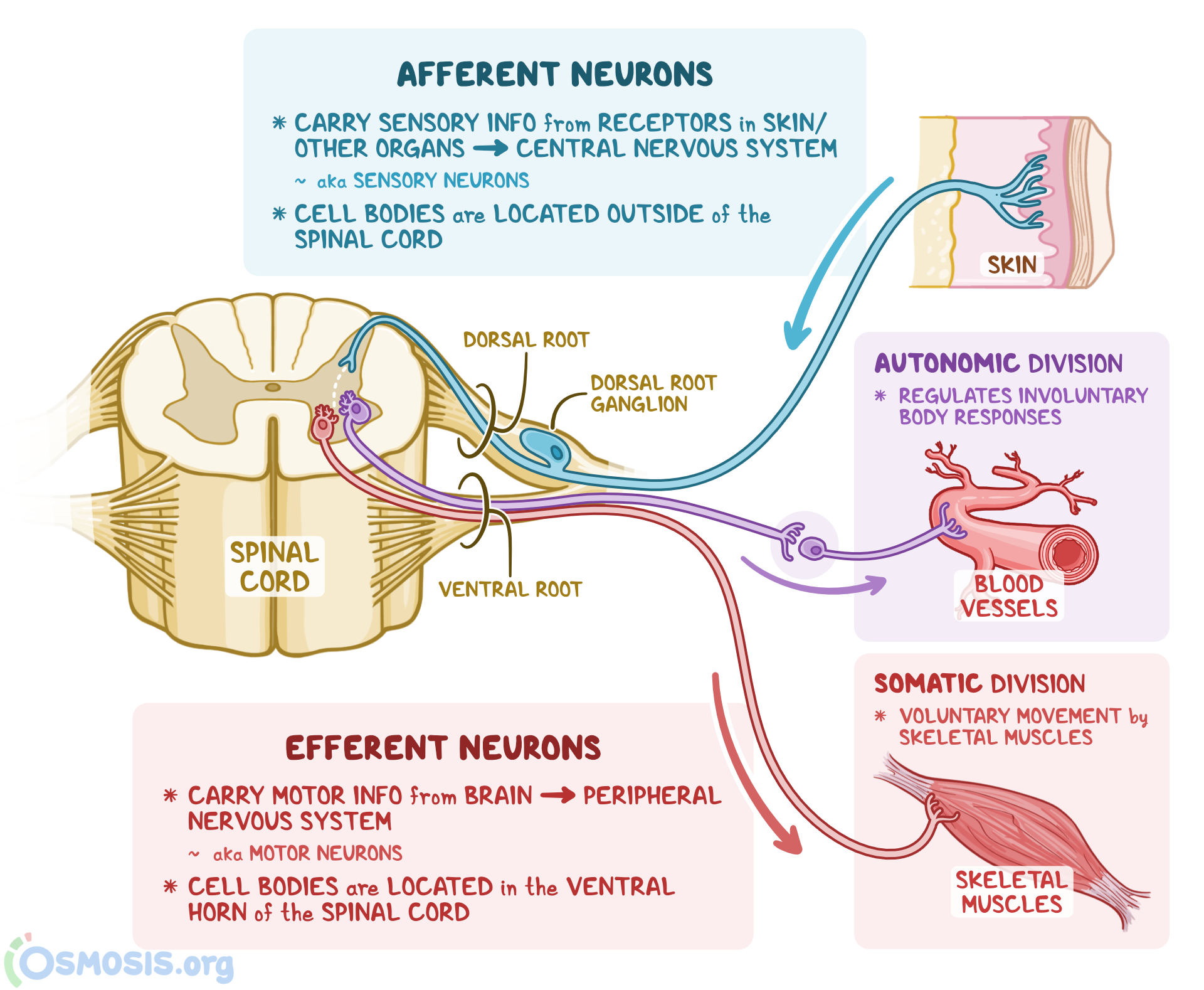
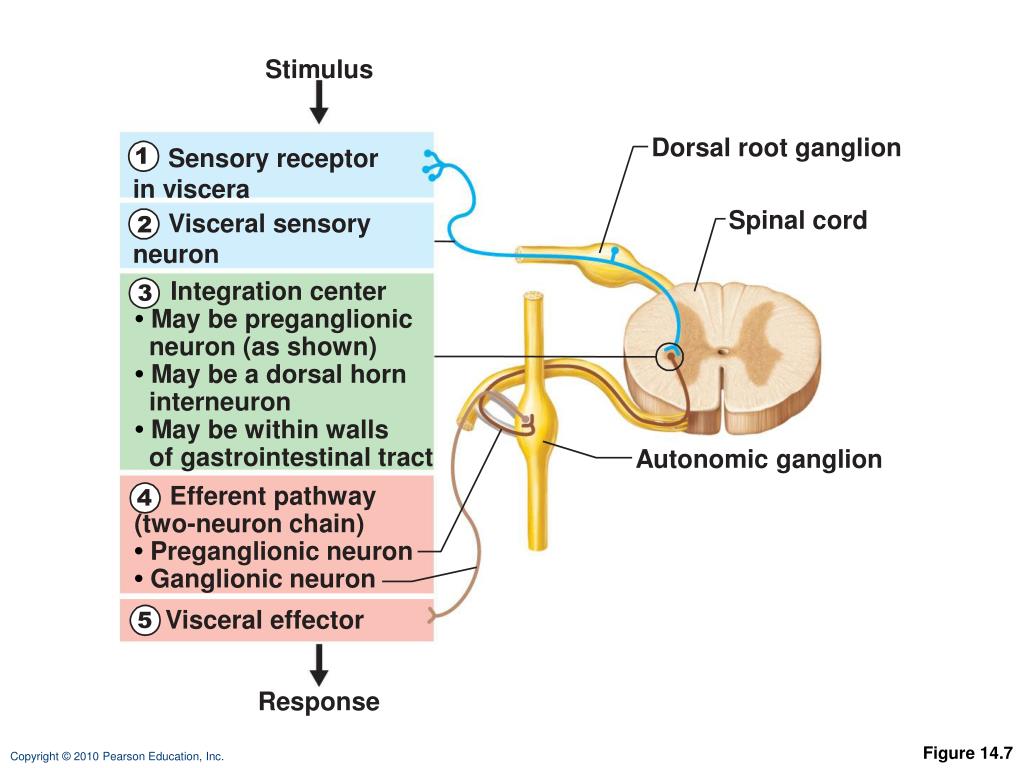
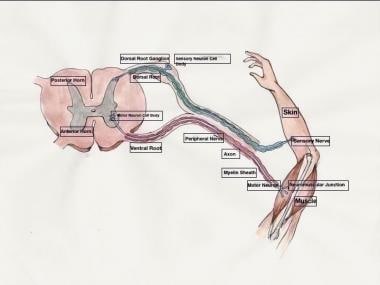
The sensory division is a part of peripheral nervous system it runs from sensory organs to the CNS brain and spinal cord. The sensory or afferent division of the peripheral nervous system provides the central nervous system brain and spinal cord with sensory information about the somatic senses tactile thermal pain and proprioceptive sensations and special senses smell taste vision hearing and equilibrium. The efferent or motor division transmits impulses from the CNS out to the peripheral organs to cause an effect or action.
Afferent division - Consists of nerve fibers that convey impulses to the central nervous system from sensory receptors located throughout the body. The somatic nervous system consists of afferent nerves or sensory nerves and efferent nerves or motor nerves. Send signals to the brain from the periphery.
The efferent division sends information from the nervous system to the organs of the body which then carry out the appropriate response. Last but not least we have reached the autonomic division of the peripheral nervous system ANS.
The somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
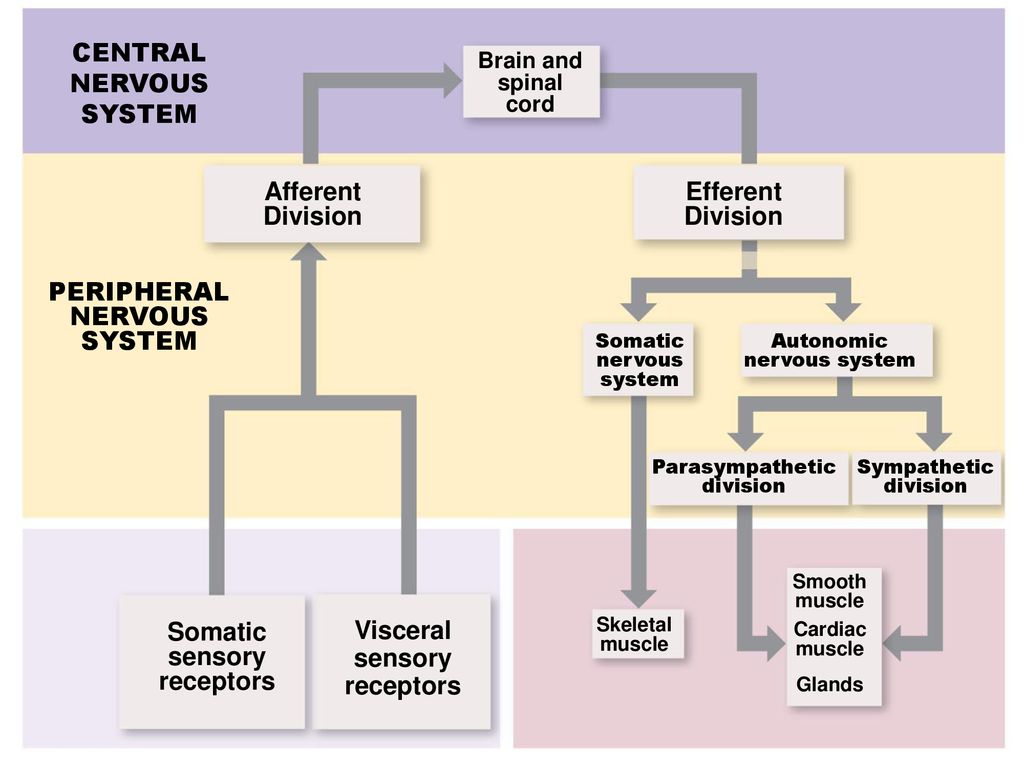
The sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division. Receptors - an end organ or a group of end organs of sensory or afferent neurons specialized to be sensitive to stimulating agents as touch or heat. It can be further subdivided into somatic and visceral divisions. The afferent division consists of neurons that are bringing sensory information about the periphery toward the CNS while the efferent division consists of neurons that are conveying information away from the CNS and out to control muscles and. Send signals to the brain from the periphery. It is involuntary in nature meaning that we have no conscious control over it. From the periphery CNS Afferernt fibers. Central nervous system CNS Peripheral nervous system PNS Sensory afferent division Motor efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system ANS Somatic sensory Visceral sensory. The sensory or afferent division of the peripheral nervous system provides the central nervous system brain and spinal cord with sensory information about the somatic senses tactile thermal pain and proprioceptive sensations and special senses smell taste vision hearing and equilibrium.
Sensory nerves contain only afferent fibers long dendrites of sensory neurons. The peripheral nervous system is itself classified into two systems. The peripheral nervous system PNS is made up of nerves and inside the nerves are neurons nerve cells that conduct action potentials between the CNS and peripheral organs. The efferent or motor division transmits impulses from the CNS out to the peripheral organs to cause an effect or action. Central nervous system CNS Peripheral nervous system PNS Sensory afferent division Motor efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system ANS Somatic sensory Visceral sensory. The sensory afferent division carries sensory signals by way of afferent nerve fibers from receptors in the central nervous system CNS. The sensory division is a part of peripheral nervous system it runs from sensory organs to the CNS brain and spinal cord.

















/what-is-the-peripheral-nervous-system-2795465-FINAL-b69e1bb803654212a83d9e68eb4847d0.png)








Post a Comment for "The Sensory (afferent) Division Of The Peripheral Nervous System"